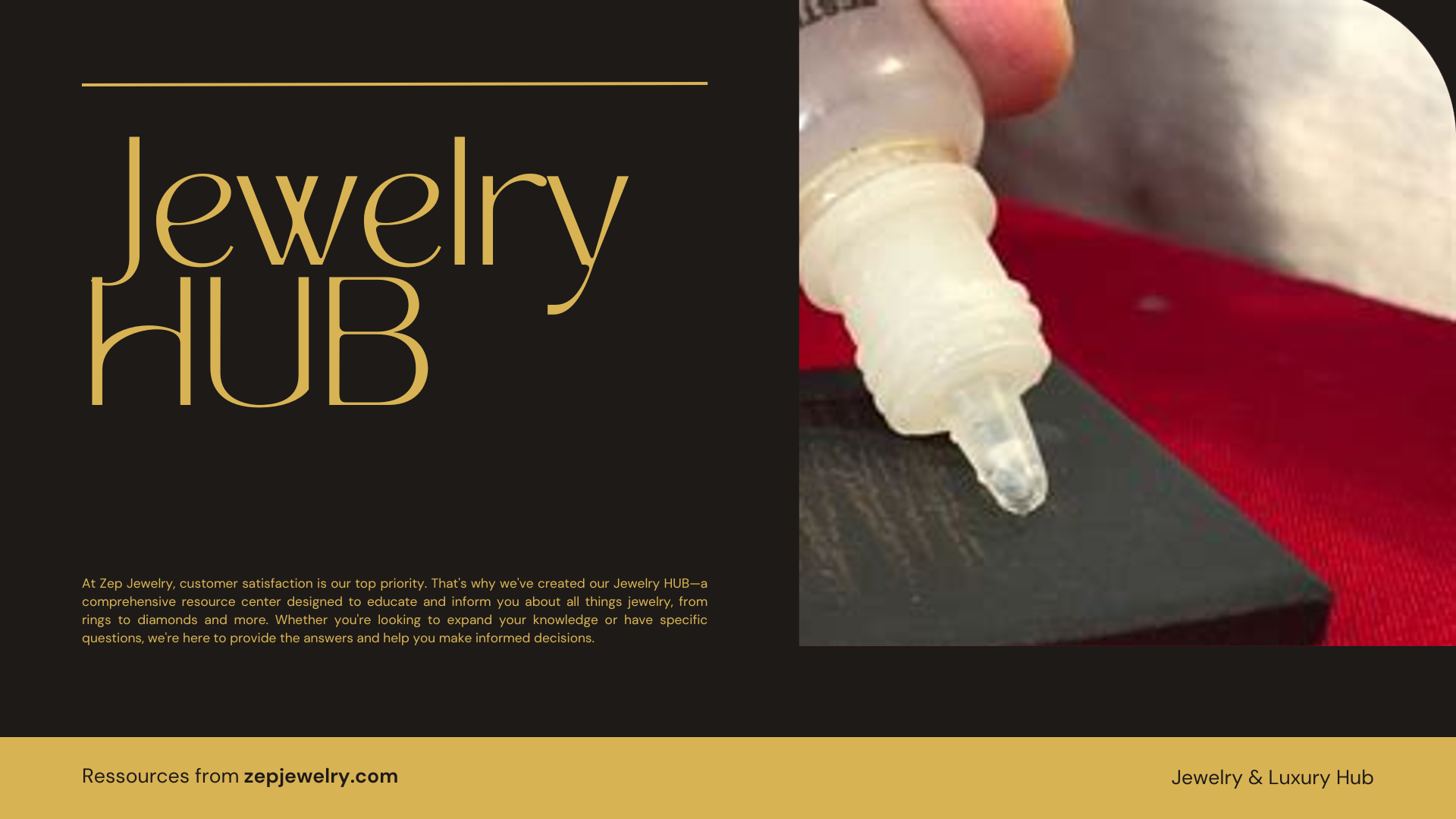
Have you ever wondered how jewelers can confidently declare a ring “real gold”? Picture this: a skilled craftsman armed with a tiny vial of acid, ready to unveil the secrets of precious metal purity. In the intricate world of jewelry, where authenticity is paramount, acid testing emerges as a time-honored method to distinguish genuine gold from imposters. This age-old practice not only combines chemistry with artistry but also plays a crucial role in maintaining trust between the buyer and seller. As we delve deeper, we’ll explore the nuances of acid testing and the importance of hallmarks in confirming gold’s authenticity in jewelry stores.
How do jewelry stores use acid testing to verify gold authenticity?
Jewelry stores utilize acid testing as a reliable, traditional approach to verify the purity of gold. This established technique involves making a small scratch on a discreet area of the jewelry piece and then applying a drop of a carefully formulated acid solution. Each type of acid is calibrated to react with gold of specific purity levels. For instance, using a solution tailored for 10k gold would yield different results than one meant for 18k gold. If the gold piece undergoes a noticeable reaction—such as changing color or, in extreme cases, dissolving—it can indicate that the item may not be genuine gold.
It’s crucial to approach acid testing with caution, as it has the potential to damage your jewelry, especially if it’s a cherished family heirloom or a high-value piece. Therefore, jewelers often recommend this method primarily as a preliminary test rather than a conclusive one. Considering the importance of preserving the integrity and market value of jewelry, many professionals will follow up acid testing with additional methods such as visual inspections or non-destructive technologies like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) testing.
Moreover, proper knowledge of the testing process can empower customers as they engage with jewelers. Understanding that a strong reaction to acid may signify a lower purity level helps buyers make informed decisions when purchasing gold pieces. This awareness also fosters trust, as customers can feel confident that their jewelry is being accurately assessed and valued. Therefore, while acid testing remains a valuable tool in the verification process, it’s often best used in conjunction with comprehensive testing strategies that jewelers provide.
What role do hallmarks play in confirming gold authenticity at jewelry stores?
Hallmarks play a vital role in verifying the authenticity and purity of gold jewelry, acting as a trusted source of information for both jewelers and consumers alike. These stamps, such as “18k” or “24k,” indicate the gold content in the piece, offering assurance about its quality. For instance, 24k denotes pure gold, while 18k contains 75% gold, with the remainder being other metals. On the other hand, markings like GP, GF, or GE reveal that a piece is gold-plated rather than solid gold, which is essential for consumers to understand, especially when making an investment.
When jewelers assess jewelry, they often inspect the less visible areas, such as the interiors of rings, bracelet clasps, or the backs of pendants, for these crucial hallmark markings. This initial inspection serves as a reliable first step in authentication before turning to more complex testing methods, like acid testing or X-ray fluorescence. Understanding hallmarks can significantly empower consumers by providing them the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions regarding gold jewelry.
Moreover, recognizing these stamps is more than just verifying gold content; it can also enlighten consumers about the manufacturer, fostering trust in their purchase. In a market where the demand for gold is ever-increasing, and where counterfeit pieces can often slip through the cracks, awareness and knowledge about hallmarks are indispensable. An educated consumer is less likely to be misled, resulting in more confidence and satisfaction in their jewelry investments. Remember, when in doubt, consulting with a reputable jeweler regarding hallmarks can enhance your understanding and ensure you’re getting the real deal.
How do jeweler experts use non-destructive testing methods like X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)?
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) testing stands out as a non-destructive method of analyzing gold content in jewelry. Unlike traditional testing techniques, XRF allows jewelers to accurately identify the gold’s purity while preserving the item’s integrity. This method reveals trace elements, which not only measure the quality but also affect health and valuation. Such advanced technology builds trust, especially for high-value items, making it a preferred choice in professional jewelry assessments.
Can DIY tests for gold authenticity be reliable, or should one always consult a professional?
While DIY tests—like the magnet or vinegar tests—can provide initial insights into gold authenticity, they often lack the accuracy of professional assessments. Techniques such as scratching gold on ceramic can indicate authenticity through color change; however, these methods can be misleading. Engaging with a professional ensures a thorough evaluation of the piece’s purity, providing consumers with peace of mind and confidence in their investment in genuine gold jewelry.
Why is it crucial for pawnbrokers to have expertise in gold testing methods?
Pawnbrokers’ skill in accurately assessing gold authenticity is vital, particularly given the rising demand for pawnshop loans during economic uncertainty. Their knowledge allows them to employ a blend of methods ranging from visual inspections to advanced techniques like XRF testing for comprehensive validation. This expertise fosters consumer trust, ensuring fair valuations of jewelry being pawned and protecting the financial interests of both the pawnbroker and the client.
What are some common misconceptions about the gold testing methods used in jewelry stores?
Many consumers believe that basic tests like the vinegar test or magnet tests can reliably confirm gold authenticity. However, while these methods serve a purpose, they can lead to inaccuracies. True gold does not respond to nitric acid, and its density prevents it from floating; these factors need to be assessed with more nuanced methods. Understanding the limitations of these tests versus the depth provided by professional methods helps consumers gain a more accurate picture of their jewelry’s authenticity.